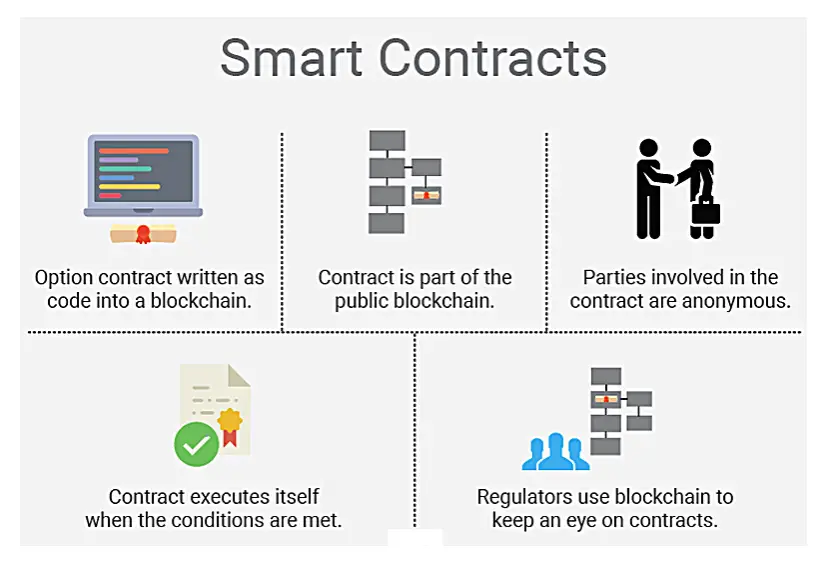
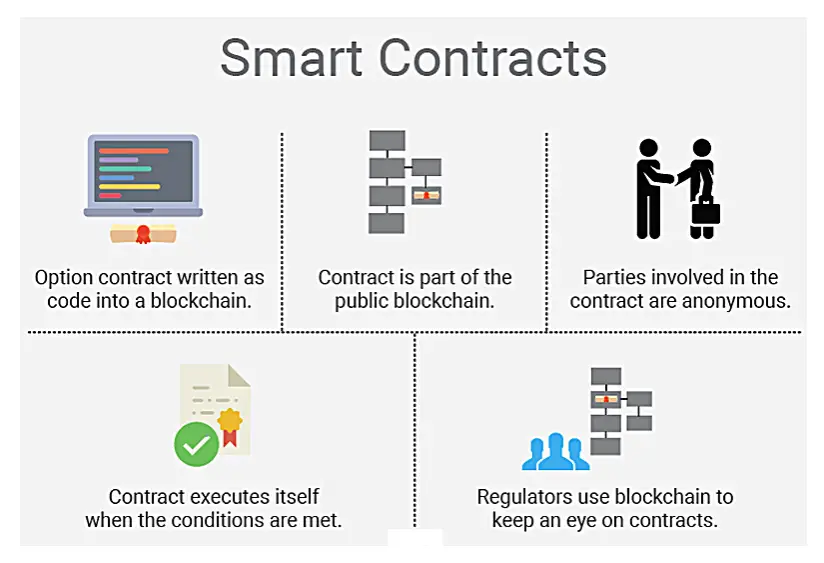
Many people these days do not have a clear understanding of Smart Contracts.
Here at Digitalogy, after working on more than 50+ Blockchain projects, try our best to explain: What are Smart contracts?
Smart contracts assist you to swap money, property, shares, or anything of value in a transparent, conflict-free way while avoiding the services of a middleman.
The most excellent way to explain smart contracts is to distinguish the technology to a vending machine.
Normally, you would go to a lawyer or a notary, pay them, and stay while you get the document. With smart contracts, you just drop a bitcoin into the vending machine (i.e. ledger), and your escrow, driver’s license, or anything drops into your account.
More so, smart contracts not only label the rules and penalties around an agreement in a similar way that a traditional contract does, but also automatically implement those obligations.
A smart contract is a computer code consecutively on top of a blockchain containing a set of rules under which the parties to that smart contract agree to interrelate with each other.
If and when the pre-defined rules are met, the agreement is automatically imposed.
The smart contract code facilitates, verifies, and enforces the negotiation or routine of an agreement or transaction. It is the simplest form of decentralized automation.
The term smart contract is a bit unfortunate since a smart contract is neither smart nor are they to be puzzled with a legal contract.
A smart contract can only be as elegant as the people coding taking into account all available information at the time of coding.
While smart contracts have the perspective to become legal contracts if certain conditions are met, they should not be baffled with legal contracts accepted by courts and or law enforcement. However, we will probably see a union of legal contracts and smart contracts come forward over the next few years as the technology becomes more mature and extensive and legal standards are adopted.
Smart Contracts are –
Self-verifying
Self-executing
Corrupt resistant
Smart Contracts can
Turn legal obligations into automatic processes.
Guarantee a greater degree of security.
Reduce reliance on trusted intermediaries.
Characteristics of a Smart Contract
Smart contracts are talented in tracking performance in real time and can bring great cost savings. Compliance and calculating happen on the fly. In order to get exterior information, a smart contract needs information oracles, which nourish the smart contract with outside information.
Types of Smart Contracts:
Blockchain and smart contracts have the perspective to interrupt many industries.
Use cases can be brought into being in banking, insurance, energy, e-government, telecommunication, music & film industry, the art world, mobility, education and many more. Smart contract utilizes cases range from simple to difficult.
Decentralized autonomous organizations, on the other hand, are the most complex appearance of a smart contract. The DAO in 2018 was an example of such a multifaceted smart contract.
Smart Contract Coding
Solidity is a smart contract programming language.
The syntax is similar to that of JavaScript, and it is designed to compile to code for the Ethereum Virtual Machine, to generate contracts for voting, crowdfunding, blind auctions, multi-signature wallets and more.
A smart contract, also known as a crypto contract, is a computer program that directly controls the transfer of digital currencies or assets between parties under certain circumstances
A smart contract not only defines the rules and penalties linked to an agreement in the same way that a usual contract does, but it can also automatically impose those obligations.
Smart contracts are tricky, and their potential goes past the simple transfer of assets — they can implement transactions in a broad range of fields, from legal processes to insurance premiums to crowdfunding agreements to financial derivatives.
Smart contracts have the potential to disintermediate the legal and financial fields; in particular, by simplifying and automating routine and repetitive processes for which people currently pay lawyers and banks sizable fees.
The task of lawyers could also change in the future as smart contracts gain traction in areas from adjudicating conventional legal contracts to producing customizable smart contract templates. Additionally, smart contracts’ capability is not only to automate processes but also to be in charge of behavior, as well as their potential with real-time auditing and risk assessments, can be advantageous to compliance.
Smart Contract History and Creation
The notion of smart contracts was first proposed by Nick Szabo in 1986. Szabo is a legal scholar and cryptographer known for laying the foundation for a digital currency.
Back then, there was little interest or activity in smart contracts because there was no digital platform or distributed ledger that could carry them.
In 2009, the cryptocurrency Bitcoin was developed via a blockchain platform comprised of a digital and distributed ledger that tracks economic transactions.
This technology enabled the development of a smart contract code that is worn to enter all the terms of the contract into the blockchain.
Many platforms now agree to the use of smart contracts, including Ethereum, Bitcoin and Nxt. Today, with the increasing adoption of bitcoin and the support of blockchain technologies, smart contracts are growing in popularity, often built on top of digital currencies to generate payments.
Smart Contract Applications And Blockchain
Blockchain is perfect for storing smart contracts because of the technology’s security and immutability.
Smart contract data is encrypted on a common ledger, making it not possible to lose the information stored in the blocks.
Another advantage of blockchain technology being integrated into smart contracts is flexibility.
Developers are able to pile up about any type of data within a blockchain, and they have a broad variety of transaction options to prefer from during smart contract deployment.
Smart Contract Advantages And Disadvantages
There are quite a few potential business advantages by means of smart contracts.
Cost-efficiency: Smart contracts eradicate many operational expenses.
Processing speed: Smart contracts run on automated processes and, in the majority cases, can abolish human involvement, increasing the speed of business transactions stipulated in the contract.
Autonomy: Smart contracts are performed without human intervention by the network, eliminating the call for and connected the risk of a third party being mixed up in smart contract deployment.
Reliability: Data entered in the blockchain cannot be altered or deleted. If one party does not complete its obligations, the other will be secluded by the conditions of the smart contract. The automated transactions also eliminate the potential for human error and make sure accuracy when executing the contracts.
This is all about Smart contracts, still in doubt whether to invest in your next startup or scale your existing business solution? Check out our curated list of Top Blockchain development agencies and start your project with them via Digitalogy now (and avail special discounts).
P.S here are some interesting similar blogs that you can read: What is Sidechain Blockchain, Atomic Swaps and STO’s.