The Blockchain is an immensely hot topic around the world of late, however, for many, the technology remains an elusive thought (or concept). Yet, it shouldn’t, the concept is easy once you get your head around the design or architecture and theory of basic crypto economic. Once you do have your “Aha” moment, the world will never seem similar again. From 20 Gigabytes in August 2014, The Blockchain has almost grown tremendously to 100 Gigabytes in 2017…
This Blockchain basics guide is meant to deliver a transparent, non-technical introduction to at least one of the most transformational & misunderstood technologies of our time. If you would like to understand what Blockchain architecture is and its potential impacts, without any technical jargon, then this post is for you.

Bitcoin vs Blockchain: Connection
“[Blockchain] is to Bitcoin, what the internet is to email. A big electronic system, on top of which you can build applications. Currency is just one.”— Sally Davies, FT Technology Reporter.
Bitcoin initially appeared during a 2008 report authored by an individual, Satoshi Nakamoto. The report/white paper elaborated an innovative P2P electronic money system known as Bitcoin that enabled online payments to be transferred directly, without a mediator. While the proposed bitcoin payment system was exciting and innovative, it was the mechanics of how it functioned that was really revolutionary. After the white paper’s publishing, it became clear that the most technical innovation wasn’t the digital currency itself however the technology that lay behind it, known famously nowadays as a blockchain.
Although ordinarily related to Bitcoin, blockchain technology has several alternative applications. Bitcoin is just the primary and most well-known uses. In fact, Bitcoin is barely one among eleven hundred applications that leverage the blockchain software package nowadays.
One example of the evolution and wide application of blockchain, on the far side digital currency, is the development of the Ethereum public blockchain, that is providing ways on how to execute P2P contracts.
What’s Under the Blockchain’s Hood?
The basic definition of Blockchain is that it is basically a kind of database. A database with built-in validation. It contains records called as blocks and further these blocks are connected to each other. They basically use cryptography to get linked to each other. Each block refers to the previous block and that’s how they are connected in a chain-like structure, and that’s where the name blockchain (blocks connected in a chain) came from. It is a distributed database but not copied and it is said to be distributed because it is existing on many networks/systems and still anyone can attain a copy of the existing records.
These blocks are very safe and secure in the databases and only the person in the network can enjoy or access these databases. These ledgers are updated on a regular basis. Ledgers are nothing but a fully connected database. Older records are preserved and new records are added on these ledgers and as I said earlier only the people in the network can access these ledgers. Since blockchain is a permanent database and can be used by many existing networks and is called Mutual distributed Ledger (MDL). Blockchains are transparent in nature and further cannot be corrupted.
Blockchain stands as proof of all transactions that have occurred on the Bitcoin network and hence, is taken into account as its main technological innovation. The current part of the blockchain records the recent transactions and once completed, goes to the Blockchain as permanent database once completed. A brand new block is generated every time a block gets the completion.
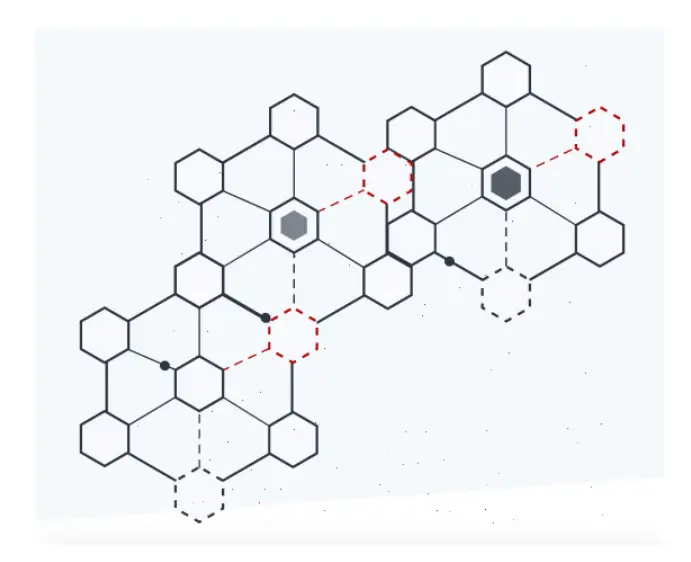
So, are the blocks placed indiscriminately in Blockchain? No, they are linked properly in a very linear, sequential order containing an association of the previous block. Taking standard banking as a thought, the blockchain is sort of a complete history of banking transactions. In a blockchain, the Bitcoin transactions are entered in a sequential manner just the way the banks’ transactions are entered. Meanwhile, the blocks are like individual bank statements.
Which Industries Can/Will Blockchain Revolutionize?
The blockchain is a distributed database technology, which is used to maintain a continuously growing list of records. Applications for Blockchain technology are growing daily.
Scope for Block Chain in the field of Banking:
The World’s central banks are being encouraged to a stock of the challenges opportunities posed by the Blockchain technology. According to one of the renowned brand in the accounting sector Deloitte, Blockchain has four main uses in the banking sector:
1. Speeding up and simplifying cross-border payments
2. The future of share trading
3. It will help in improving online identity management.
4. Loyalty and Rewards.
Applying Block Chain in Real Estate:
It is the next technology for conveying title to real property. Below we will also look at three ways that blockchain could disrupt the real estate market: by speeding up the system, providing additional transparency and offering safer investments to everybody concerned.
1. Expediting the Process
After a period of “slow” sales in 2014, house prices have up to the extent that in fall 2015, some consultant warned the housing market was entering a bubble far worse than seen in the run-up to the Great Recession. Demand for homes is higher than ever, and with less new constructions being engineered, prices for existing properties are hiking up. Despite slight sales hiccups in September 2015, experts predict that prices are going to keep on rising.
The Blockchain will do little to influence local legislators’ sales restrictions, it’ll have a good impact on the financial verification element of the sales process itself. At current, most consumers and sellers make use of escrow and title companies for 3rd party verification — a safety net to make sure both parties keep their end of the deal, as well as to reduce the danger of fraud.
2. Reducing Fraud
One of the main reasons that buyers and sellers have traditionally used escrow and third-party verifications is to reduce the chances of either party getting burned by real estate fraud. As reported by Morgan Brennan from Forbes, one of the most recurrent types of real estate fraud is rental scams, in which a scam-artist can copy details and photos from a real listing, then re-post on another website while posing as the agent responsible for the property.
3. Offering Total Transparency
A very little minority of people purchases houses outright and proving suitability for a mortgage or loan has to date been a nail-biting, slow method that is typically lengthened due to red tape and administrative issues. The Internet is stuffed with tips about how to speed up the method but blockchain might have the answer.
Using the Blockchain, folks can create a digital ID for a real estate asset, as well as for themselves as the customer or merchant. In this way, the mortgage process and transfer of ownership would be seamless, and much quicker than it is today.
Blockchain has applications that go on the far side obvious things like digital currencies and cash transfers. From voting, electronic smart contracts, and digitally recorded property assets to patient health records management and proof of possession for digital content.
Blockchain can deeply disrupt many industries that think about intermediaries like banking, finance, academia, real estate, insurance, legal, health care, etc— amongst several others., This can and will definitely lead to job losses and therefore the complete transformation of entire industries. However, overall, the elimination of intermediaries brings largely positive edges. Banks & governments for instance, usually impede the free flow of business due to the time it takes to method transactions and restrictive necessities. As per a recent survey conducted by one of the largest research organizations, almost 60% of the countries want Bitcoin and other Cryptocurrencies to be regulated. Read some of the concerns and arguments of its regulation here.
The blockchain will change an exaggerated quantity of individuals and businesses to trade rather more times and with more efficiency, considerably boosting native and international trade.
Blockchain technology would additionally eliminate costly intercessor fees that became a burden on people and businesses, particularly within the remittances vertical.
Perhaps most deeply, blockchain guarantees to democratize & expand the worldwide national economy. Giving those who have restricted exposure to the worldwide economy, higher access to money and payment systems and stronger protection against corruption and exploitation







